Maida
What is Maida Flour?
Maida is a finely-milled, white wheat flour commonly used in India. It is obtained from the endosperm part of the wheat grain and can be made from winter- or summer-wheat varieties.
Maida is a white flour from the Indian subcontinent, made from wheat. Finely milled without any bran, refined, and bleached, it closely resembles cake flour. Maida is used extensively for making fast foods, baked goods such as pastries, bread, several varieties of sweets, and traditional flatbreads. Owing to this wide variety of uses, it is sometimes labeled and marketed as “all-purpose flour”, though it is different from all-purpose flour.

Maida flour is very popular in India, and other Central Asian and South Asian countries. It is used in preparing breads and baked goods, noodles and other food products. Current regulations in India require fortifying the flour with iron, zinc, vitamin A, folic acid and other B-vitamins.
Origin
Maida flour is most commonly used in India, especially the Southern part of the country as well asian countries. It is one of three types of flour commonly used in Indian baking; the other two are Atta and sooji (suji).
- Maida: used in making bakery products such as pastries, sweets, as well as traditional breads such as paratha and naan
- Atta: used in making flatbreads, such as chapati, roti, naan and puri
- Sooji/suji: used in making pasta, breakfast cereals, puddings, and couscous
Function
Maida flour is low in protein (gluten), an advantage for producing high-volume, soft/tender cakes with fine grain. Its high extensibility and stretchability are desirable qualities for a variety of Indian pastries and baked goods.
Nutrition
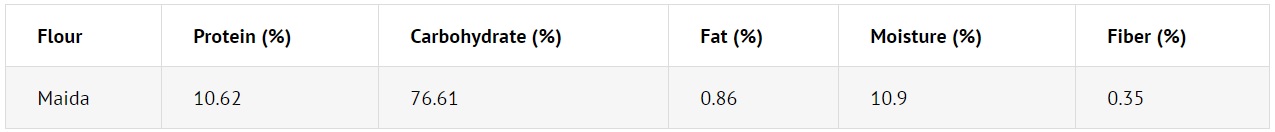
Maida flour is low in protein and fiber due to bran removal during milling.
Typical composition of maida flour:
There has been a controversy regarding bleaching maida flours with alloxan, a substance banned by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI). The chemical is a beta-cell killer and can cause diabetes in humans.
Application
Maida is used extensively in Central Asian and Southeast Asian cuisine. It is mainly used in making flat breads such as naan, tandoori roti, pizza crust, noodles, bhatoori (a fluffy, deep fried, leavened bread), cakes, biscuits and many other pastries. In addition to bakery products, it is used as a fermented batter (jilebi),4 as a sauce thickener and in coating fried food products.
Regulations
Being an Indian ingredient, maida is governed by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) which regulates its safety and nutrients fortification levels.
